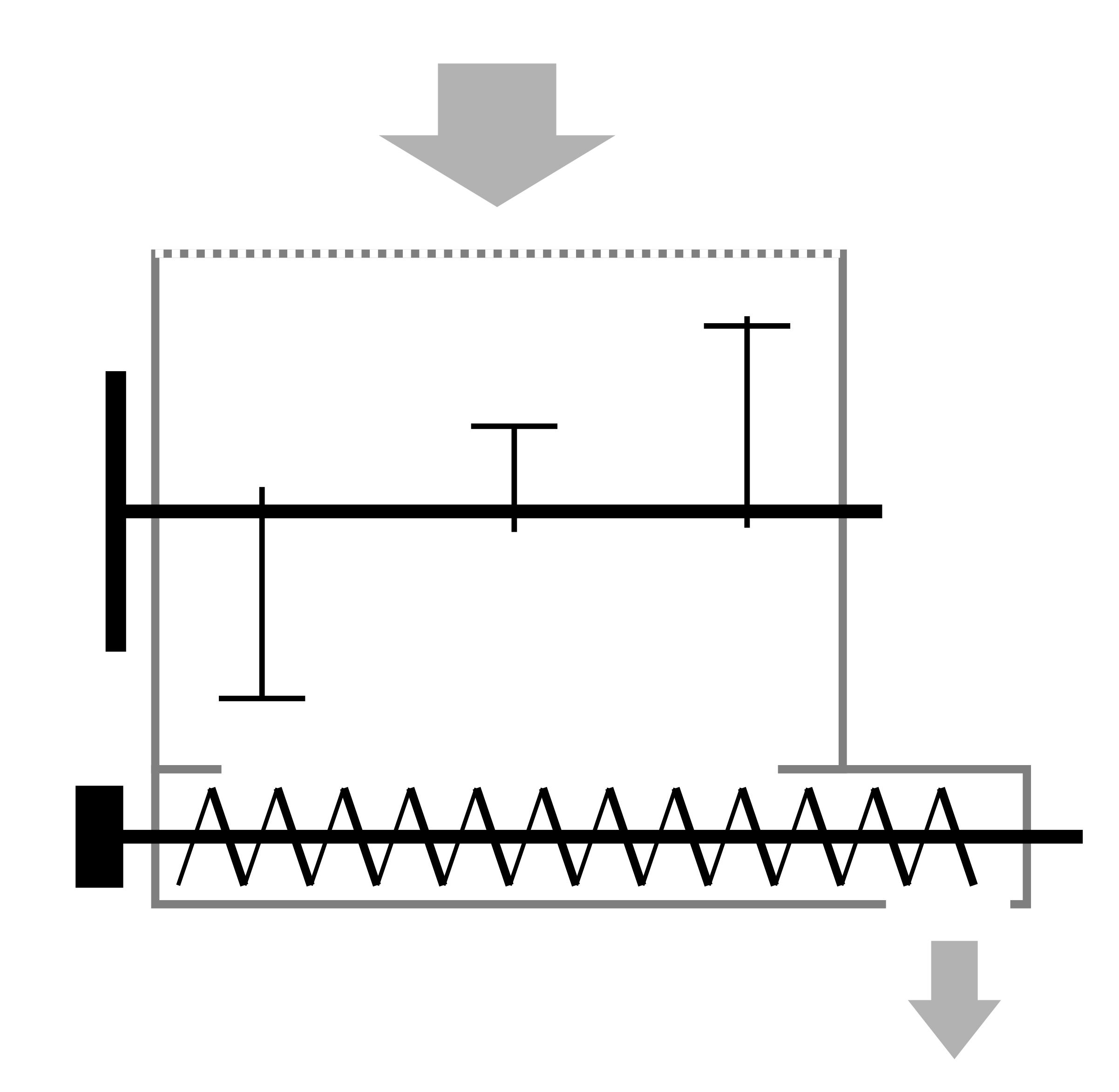
These conveyors come in two types based on their drive mechanism. The first type uses a crankshaft mechanism, which tosses the conveyor trough with a relatively low frequency of 3-4 Hz and a large amplitude. Either silentblock-supported connecting rods or spring plates firmly attached to the trough and the base act as supports. In the second type, a standard platform vibrator is used. This consists of an electric motor running at 700 or 1400 RPM with offset weights on its shaft, supported by springs. The raw material moves because it gets tossed and, in the brief moment of flight, the surface beneath it shifts backward. This results in continuous shaking in one direction.
 The maximum efficiency in moving material is achieved when there is no complete detachment of particles from the trough, but at some point, the interaction force, and thus friction, is close to zero. When calculating the crankshaft mechanism, you first determine the oscillation frequency of the trough, which depends on the support length, their angle relative to the horizon, and the amplitude of oscillations. The downward acceleration should equal or be slightly less than the acceleration due to gravity. Such calculations and adjustments allow you to transport material with minimal dust generation and without damage. If the movement involves classification on screens or requires breaking up clumps, the amplitude is increased to ensure collisions between the material and the trough body. When equipped with an industrial vibrator, these conveyors can act as pellet feeders during packaging, and when paired with screens, they serve as vibrating screens or sieves.
The maximum efficiency in moving material is achieved when there is no complete detachment of particles from the trough, but at some point, the interaction force, and thus friction, is close to zero. When calculating the crankshaft mechanism, you first determine the oscillation frequency of the trough, which depends on the support length, their angle relative to the horizon, and the amplitude of oscillations. The downward acceleration should equal or be slightly less than the acceleration due to gravity. Such calculations and adjustments allow you to transport material with minimal dust generation and without damage. If the movement involves classification on screens or requires breaking up clumps, the amplitude is increased to ensure collisions between the material and the trough body. When equipped with an industrial vibrator, these conveyors can act as pellet feeders during packaging, and when paired with screens, they serve as vibrating screens or sieves.
Advantages of vibrating conveyors:
- No expensive consumables like belts, chains, and sprockets
- Ability to move very large pieces
- Capability to work with materials at high temperatures
- Jamming and mechanical damage are virtually impossible
- The most economical option after pneumatic transport
Disadvantages of vibrating conveyors:
- Cannot handle sticky, wet materials
- Increased dust emission for loose materials
- Only allows horizontal transport
In the pellet industry, the raw material is either sticky and wet or dry and dusty, which limits its application to only a few uses. The best use is feeding slabs into the chipper. Since the slab and small timber are covered with branches on the surface, a regular rubber belt quickly wears out, especially if its speed is not synchronized with the spindles. A vibrating conveyor not only feeds without firm pressure but also helps distribute multiple logs across the surface. Without tossing, these conveyors can efficiently carry away dry wood chips, cubes, and cut-offs from woodworking machines.
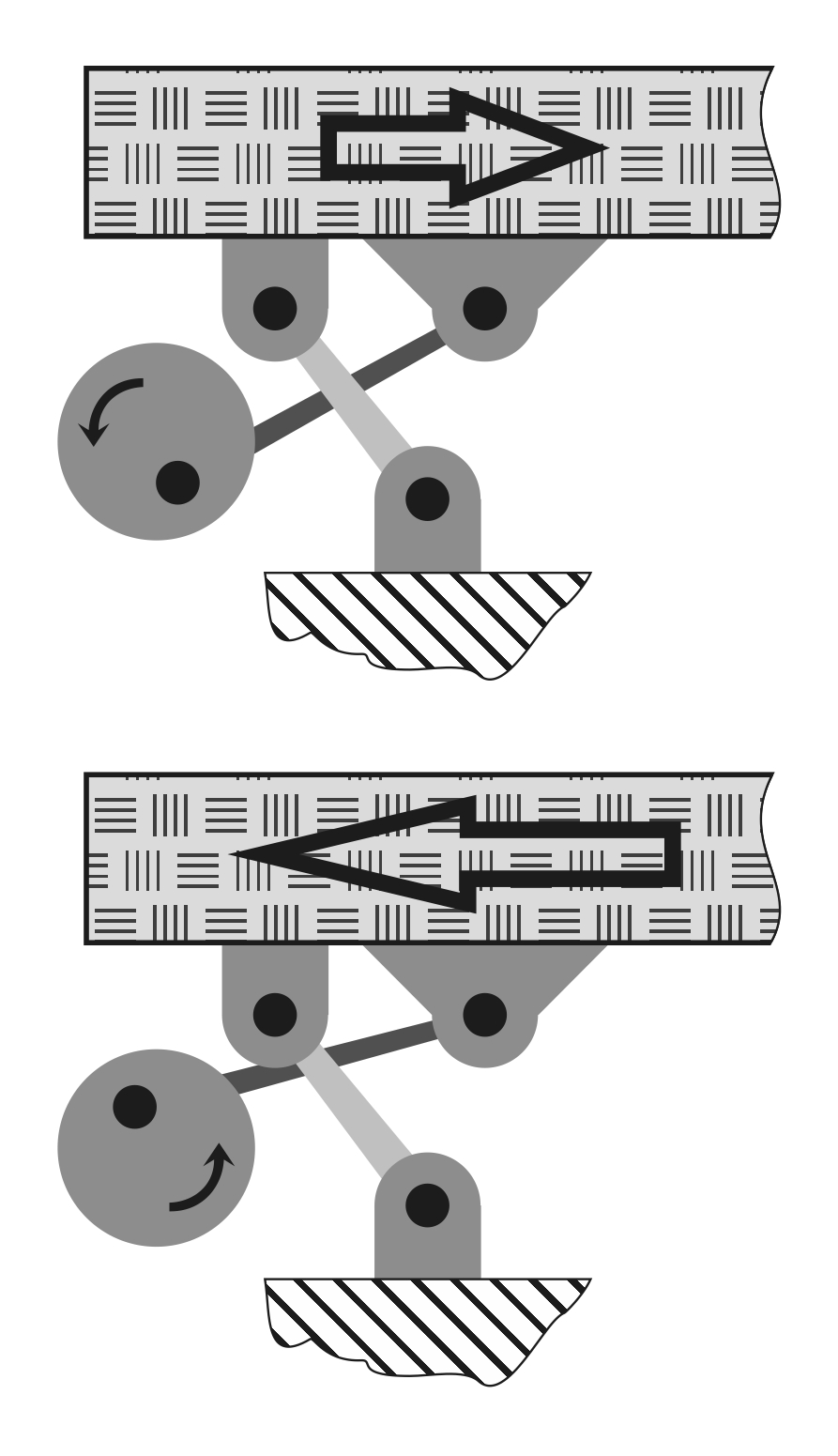 Although the main purpose of the drive is to create vibration, the direction of its rotation in any design can significantly impact efficiency and reliability. As shown in the picture, the speed of movement in different directions is not the same since the crankshaft axis is significantly offset from the motion vector. Therefore, during the upward motion, the speed is lower and the force created is greater, helping the motor to lift the trough with raw material. During the reverse stroke, the empty and light trough is pulled back more quickly, adding momentary load to the motor, bringing it to the level of the previous stroke. This rotation direction balances the average load on the drive, reduces vibration stress, and increases productivity. If turned in the opposite direction, it will lead to impact lifts that help break clumps, but due to uneven load, an additional flywheel may be needed, and the lifespan of supports will sharply decrease.
Although the main purpose of the drive is to create vibration, the direction of its rotation in any design can significantly impact efficiency and reliability. As shown in the picture, the speed of movement in different directions is not the same since the crankshaft axis is significantly offset from the motion vector. Therefore, during the upward motion, the speed is lower and the force created is greater, helping the motor to lift the trough with raw material. During the reverse stroke, the empty and light trough is pulled back more quickly, adding momentary load to the motor, bringing it to the level of the previous stroke. This rotation direction balances the average load on the drive, reduces vibration stress, and increases productivity. If turned in the opposite direction, it will lead to impact lifts that help break clumps, but due to uneven load, an additional flywheel may be needed, and the lifespan of supports will sharply decrease.
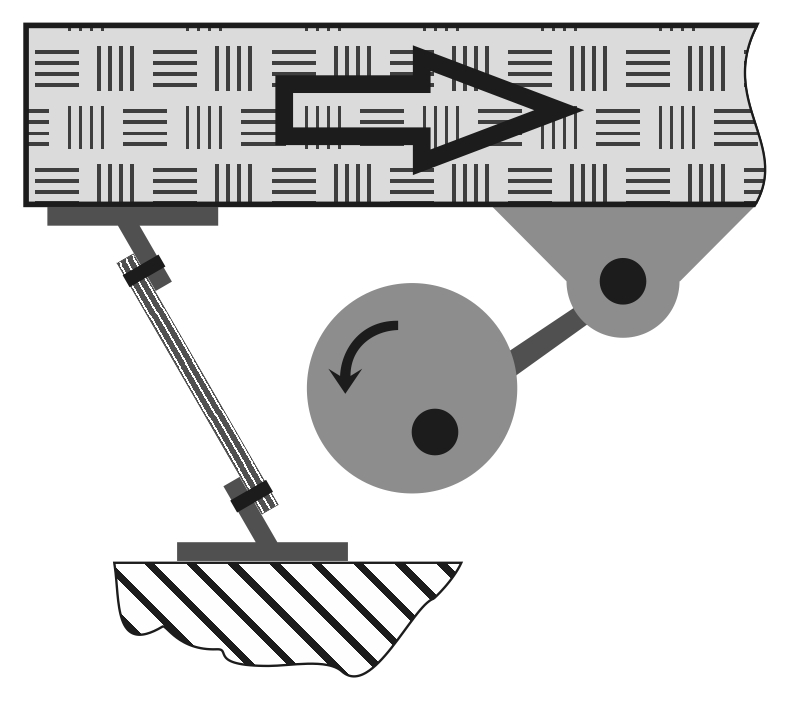 The ability to adjust the position of the drive allows customization for each type of raw material and working conditions, although it complicates the structure. Using elastic plates as supports can not only reduce costs but also improve the reliability of the conveyor. Depending on the length and load, materials such as conveyor belts, fiberglass, plywood, or spring steel can be used. When designing such supports, several features should be considered:
The ability to adjust the position of the drive allows customization for each type of raw material and working conditions, although it complicates the structure. Using elastic plates as supports can not only reduce costs but also improve the reliability of the conveyor. Depending on the length and load, materials such as conveyor belts, fiberglass, plywood, or spring steel can be used. When designing such supports, several features should be considered:
- The average position of the oscillating mechanism should correspond to the working position of the trough with loaded material. Otherwise, this mass will continuously exert pressure on the drive bearings, noticeably shortening their service life.
- Depending on the size and mass of the trough, installing counterweights on the eccentric may be beneficial to reduce variable loads on the drive mounting.
- For different materials, resistance to fatigue failure is calculated using various empirical formulas, but the actual behavior is tested in practice. For common steel, it should not exceed 40% of the yield strength load, and for hardened steel and fiberglass, it should not exceed 70% of the ultimate load.
- The material must be resistant to environmental impacts and temperatures under application conditions.